Understanding the HR Environment
Human Resource Management (HRM) is important because it directly affects whether organizations can meet their goals and provide value to stakeholders.
HRM is the set of policies, practices, and systems that guide how employees behave, feel, and perform at work.
Human Resource Management (HRM) focuses on the policies and practices that shape how people work, grow, and succeed within an organization. It covers every step of the employee journey: designing jobs, planning for staffing needs, attracting and selecting the right talent, training and developing employees, evaluating performance, rewarding contributions, and building a supportive work environment. When these practices are managed well, organizations see higher employee satisfaction, stronger customer loyalty, greater productivity, and a reputation for innovation and success.
Here are the key reasons that make HRM important:
1. Connection to Company Performance
HRM practices—such as acquiring, developing, motivating, and retaining employees—are critical to overall organizational success.
Effective HRM helps companies improve profits, productivity, quality, customer satisfaction, and innovation.
2. Strategic Role
HR is no longer just about administrative tasks—it is now a strategic partner that supports organizational strategy.
Aligning HR practices with company goals ensures long-term success.
HR plays a crucial role in business strategy and serves as a source of competitive advantage.
Key Functions:
Job Analysis & Design—defining tasks and jobs.
Recruitment & Selection—attracting and choosing the right employees.
Training & Development—building skills for current and future roles.
Performance Management—ensuring activities match goals.
Compensation & Benefits—pay, incentives, and rewards.
Employee Relations—communication, labor law, and morale.
Compliance with laws encompasses issues such as equal opportunity, safety, privacy, and labor laws.
Strategic HR—All practices aim at better company performance (higher productivity, quality, and competitiveness).
In short: HRM is important because it ensures that organizations have the right people, with the right skills, motivated in the right way, working under the right conditions—so that the company can achieve its mission, adapt to change, and remain competitive.
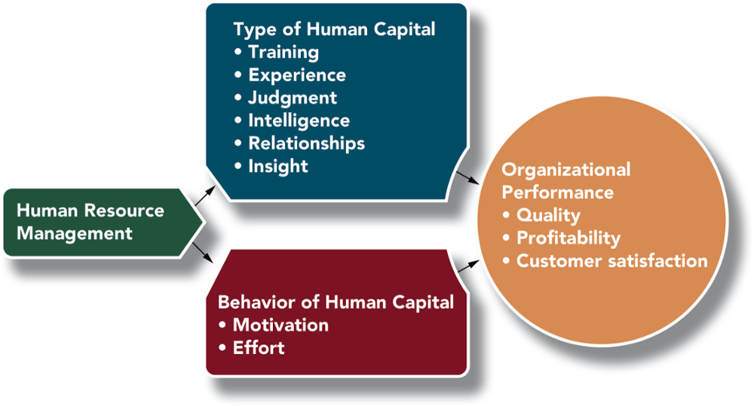
The diagram shows that Human Resource Management (HRM) impacts performance in two main ways:
Type of Human Capital – HRM shapes the knowledge, skills, and abilities employees bring, such as training, experience, judgment, intelligence, relationships, and insight.
Behavior of Human Capital – HRM also influences how employees act, especially their motivation and effort.
Together, these affect organizational performance by improving:
Quality of products and services
Profitability of the business
Customer satisfaction
In short: HRM impacts performance by ensuring employees have the right capabilities and by motivating them to put in effort, which leads to better quality, higher profits, and satisfied customers.
3. Value Creation for Stakeholders
HRM contributes value not only to shareholders but also to:
Employees: Growth, satisfaction, and career opportunities.
Customers: Better service and higher-quality products.
Communities: New jobs, ethical practices, and social responsibility.
The Environment: Through Sustainable Policies, 6th Edition.
4. Competitive Advantage
Competitive advantage is what makes a company do better than its competitors, like offering better quality, lower costs, or unique products that customers prefer.
People are often the most important resource for creating an advantage over competitors.
Human resources give organizations an advantage because:
Valuable: People’s skills and knowledge help the company succeed.
Rare: Talented people are not easy to find everywhere.
Cannot be imitated: You can’t copy someone’s exact abilities, teamwork, or creativity.
No good substitutes: Machines or systems can’t fully replace what people bring.
In short: Employees are unique and powerful resources that make a company stronger than its competitors.
A high-performance work system combines people, technology, and organizational processes so they function together effectively. Companies may create strong training programs, recruit talent with modern skills, and reward behaviors such as teamwork and adaptability.
Examples of practices:
Training programs → build needed skills.
Recruiting new skill sets → adapt to change.
Rewards for behaviors like teamwork, flexibility, and learning.
Goal: create an environment where employees perform at their best and help the company stay ahead
Key Roles of Human Resource Departments
In most organizations, the HR department manages the essential functions that keep people and business working smoothly. Its responsibilities can be grouped into three main areas:
Administrative tasks – Handling hiring, benefits, and other day-to-day employee services.
Business support – Designing HR systems that help attract, develop, and retain the right talent.
Strategic partnership – Aligning people practices with company goals to build a competitive edge.
HR also oversees activities like job design, recruitment, training, performance management, compensation, employee relations, compliance with labor laws, and workforce planning.
Analyzing and Designing Jobs
Every company needs tasks completed to deliver its products or services. These tasks are grouped into jobs. The way jobs are analyzed and designed affects efficiency, quality, and the kind of employees needed. Some jobs may be very simple with limited tasks, while others are broad and require multiple skills. Modern organizations often favor broader jobs or even team-based work to encourage innovation and quality.
Job Analysis: Finding out detailed information about what a job involves.
Job Design: Deciding how the work will be done and what tasks the job includes.
Recruiting and Hiring Employees
Once a company knows the type of workers it needs, it looks for candidates and decides who to hire. This process has two main steps: recruitment, which is attracting people to apply, and selection, which is choosing the best fit for the job. Companies may recruit externally through job boards, social media, or college events, or internally by promoting and referring current employees.
Recruitment: Finding and attracting people who may want to work for the organization.
Selection: Choosing the right people with the skills and qualities needed to help the company succeed.
Training and Developing Employees
Organizations hire people for their skills, but employees often need to keep learning to stay effective. Training helps workers do their current jobs better by teaching job-related knowledge, skills, and behaviors (like safety training). Development prepares employees for future roles and changing job demands, often focusing on leadership, teamwork, and adapting to customer needs. Companies may train everyone or invest more in specific employees depending on their goals.
Training: A planned effort to teach employees the skills and knowledge needed for their current job.
Development: Building skills and abilities that prepare employees to grow and handle future challenges.
Managing Performance
Performance management is about making sure employees’ work supports the organization’s goals. It involves setting clear job tasks and outcomes, measuring how well employees perform, and comparing results with expectations. Feedback and rewards are then used to encourage improvement and recognize success. Evaluations may look at behaviors (what employees do), results (what they achieve), or both, and can include input from supervisors, peers, and even the employees themselves.
Performance Management: The process of making sure employees’ work and results match the organization’s goals.
Pay and Benefits
Pay and benefits are key tools for motivating employees and supporting company strategy. High pay can help attract top talent for innovation and service, while careful planning helps control costs in low-cost strategies. Decisions include how much to give in base pay versus performance-based rewards and which benefits to offer (like health insurance, retirement plans, or paid time off). Administering pay and benefits also requires accurate systems for record keeping and clear communication with employees. But money alone is not always enough—organizations also need to consider non-financial rewards such as recognition, growth opportunities, and a positive work environment.
Pay and Benefits: The salary, incentives, and extra rewards employees receive, which motivate them and support the organization’s goals.
Managing and Using HR Data
HR departments must keep accurate and private records of employee information, from job applications to performance and benefits. Good data management ensures compliance with laws, protects privacy, and supports better decision-making. Modern systems turn employee information into insights through workforce analytics, which uses data and scientific methods to find patterns—for example, identifying top talent, predicting hiring needs, or seeing which roles perform best.
Workforce Analytics: Using data and quantitative tools to make evidence-based decisions about employees that support business goals.
Compliance with Labor Laws
HR plays a key role in making sure organizations follow government rules about equal opportunity, pay, benefits, safety, privacy, and job security. This includes filing reports, posting notices, and preventing unlawful practices. Because laws change quickly, HR must stay updated and adjust policies to protect both the company and employees. Issues like privacy rights, job security, and age discrimination are becoming more important as the workplace evolves.
Compliance with Labor Laws: Making sure the company follows all rules and regulations that protect employees and guide fair workplace practices.